Table of Content
It wouldn’t be wrong to say, a legacy ERP is nothing but an outdated technology that was an innovation once. Most ERP Systems were created in the 1980s or early 1990s and are often based on older technology. It was a Pre-Cloud Era which is easy to characterize – accessed via LAN, with limited reporting capabilities and business intelligence not intended for digital innovation, implemented on-premises (manual and time-consuming implementation), and lacks customizations.
What is an ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a software used by businesses to manage their day-to-day activities like procurement, accounting, operations etc. This set of tools integrates, automates and streamlines different functions of the organization which results in better productivity.
An ERP provides a unified view of the organization which results in informed and strategic decision making. It provides a centralized database that helps businesses to access real time information and generate useful reports.
Let’s have a quick look at the current ERP market statistics:
- The annual global market for ERP software is more than $25 billion and is expanding by 10 to 20 percent.
- The global ERP software market expanded by 9% in 2019, with an estimated $39 billion in global software revenue as a result.
- The ERP industry is still seeing tremendous growth, and by 2025, analysts anticipate that it will reach a value of about $49.5 billion.
- ERP and CRM were both ranked as investment priorities by 53% of IT decision-makers.
Types of ERP Systems
On-Premises ERP System
On-Premises ERP System is a system that runs on the clients/businesses server and involves an inhouse IT team and infrastructure to maintain it. The businesses can control the operations and acquisition of servers and storage. It means higher investments in terms of cost and time frames.
On-Cloud ERP System
In On-Cloud ERP System, the software is available on license model and the ERP service providing company owns the server. The ERP is hosted on the company’s server which ensure no maintenance cost for the business and these servers are highly secured that reduces the chances of data leak or break.
Hybrid ERP System
The hybrid ERP system is a combination of cloud and on-premises ERP systems. With this technology, a company can continue to run vital business applications as well as those with their own set of technical constraints or unique requirements. They carry out this in-house or through a private cloud setup. Users have simultaneous access to other applications or application components on public clouds.
What is a Legacy ERP System?
A legacy ERP system that once was a boon is an outdated technology in the modern business world. Though they served well in improving the business productivity and streamlining their operations, the modern business now calls for way more than what a legacy ERP system can offer.
Now, it’s about businesses moving to the cloud for managing their operations which transforms the way you manage your operations and take advantage of the new opportunities the Cloud has to offer.
Here are reasons why Legacy ERP Systems are hampering the growth of the business
- Legacy ERP Systems manage your businesses from traditional computers and servers, which don’t suit modern business requirements.
- Legacy ERPs cannot offer the scalability, flexibility, and adaptability that modern businesses require.
- Legacy ERP Systems have compatibility and integration issues with modern technological advancements.
- The operating costs of a Legacy ERP system are huge and scaling the system is a complex and time taking process.
- Legacy ERP Systems require many IT resources to manage them, wherein Cloud ERP systems give the flexibility to operate with no such obligation.
Definition of Modern/Cloud ERP
Take the opposite scenario of all the above, modern/cloud ERP systems are based on modern programming languages, cloud-based, accessible through any device, easily customizable, and advanced enterprise-wide business reporting with real-time data and AI Capabilities.
Less investment in Infrastructure
With the coming of cloud solutions, businesses no longer need to worry about the required hardware and software for business functioning. There is no need of worrying about software and system updates and about situations that involve ensuring high system availability, backups, etc.
Compared to on-premises deployment, cloud infrastructure makes it simple to set up extra environments for various uses, such as development, testing, performance testing, etc. (additional environments in the cloud infrastructure are of course associated with additional costs).
Ease of Customizations
Customizing a legacy ERP was a complex task and involved high efforts to upgrade from the older to a newer version which was a point of concern for the businesses and led to fewer upgrade subscriptions.
In cloud ERP the system updates happen periodically and regularly from the vendor’s side and the businesses are always on the updated version of the tool and need not worry about customizations. It has become relatively easy for businesses to adapt to the newer version of the ERP.
In legacy ERP the standard code could always be changed but Cloud ERP doesn’t come with that functionality perhaps they can write their own code known as extension in the predetermined places in the program code (known as extension points).
Smooth Implementation Methodology
The Advantages of this approach extend to engaging the business user at every step of the process. It helps in monitoring the progress on an ongoing basis and taking corrective actions if needed, regular feedback is gathered from the users, and in case of incremental delivery rapid implementation can be achieved.
ERPs can be easily updated
The user interface can only be used by the client and the implementer to access the system. We used to be able to quickly access data, apply fixes, and carry out ad-hoc tasks, but now those options are no longer available. A new procedure is chalked out that precisely prescribes the steps to install a new package in production.
The System Offers Periodic Updates
As a result, businesses are always using the most recent update, which contains all the critical fixes as well as new functionalities and features. Implementors need to accept updates on a regular basis and ensure that all the extensions work properly.
Modern/Cloud ERP Examples
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
- NetSuite
- Acumatica
- SAP Business One
- Salesforce
- Sage Intacct
ERP Implementation Statistics
Companies need a clear understanding of the new system needs to build alignment across the organization and carry out an ERP rollout successfully. The likelihood of the project succeeding is increased by selecting the ideal vendor and appointing an internal implementation team.
- 67% of distributors and manufacturers who responded to a 2019 poll said their deployments were successful or extremely successful.
- Companies who implemented ERP successfully cited internal organizational factors such managerial support, effective change management initiatives, and due diligence as the main drivers of success.
- 49% of businesses claimed that all business operations have improved after ERP deployment. 5% of businesses only claimed not to have seen any progress.
- Midsize businesses with revenues between $100 million and $250 million had the quickest implementations, taking only 6.7 months, according to a survey on ERP adoption. Companies with annual revenues over $25 billion took approximately 12.35 months.
Modern ERP VS Legacy ERP Systems
The early ERP Systems that were majorly implemented on-premises were a cumbersome process and involved the company’s IT department and resources to be an active part of the implementation process.
ERP solutions in the cloud follow a different set of implementation methodologies from the Legacy ERP Systems. Let’s have a quick look at the differences.
Modern ERP VS Legacy ERP Systems Quick Comparison
| Legacy ERP Systems | Modern ERP Systems |
| Uses obsolete legacy programming languages | Uses Modern Programming Technologies |
| Are installed on-premises | Installation can be done on-premises or on-cloud |
| System can be accesses through connected desktops | Can be accesses through cloud-connected devices from anywhere |
| Implementation process takes time | Implementation process is quick |
| Requires lot of IT resources to maintain it | Minimal requirement of IT resources to maintain it |
| Basic data reporting | Real-time data reports can be generated with one click |
Which Industries use ERP Software most?
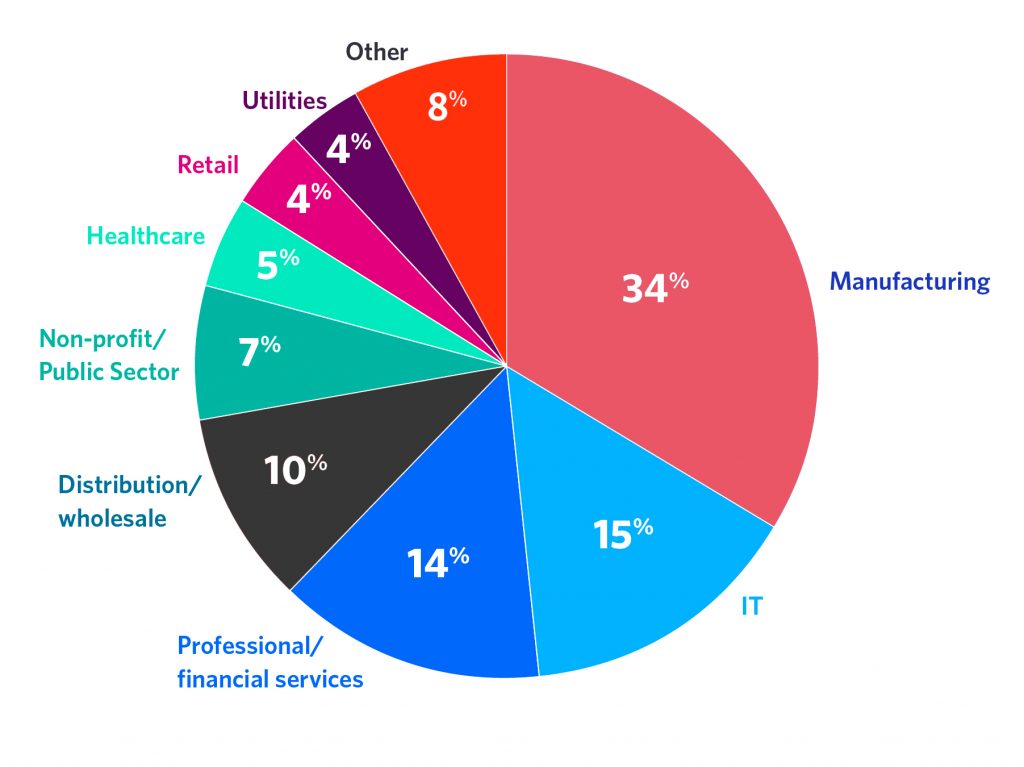
- According to a recent study, around 34% of the Manufacturing businesses uses ERP system to manage their operations.
- 15% IT Industry businesses makes use of ERP system to manage their projects.
- Professional/Financial Services to target growth and better ROI uses ERP systems, which stands at roughly 14% of the businesses in the industry.
- Roughly around 10% of the distribution and wholesale businesses use ERP to manage their supply chain management operations.
- Industries like Non-Profit Sector, healthcare, retail and utilities are also using ERP system to manage their business operations.
Why Microsoft plays a big role in Modern ERP System?
With the purchase of Navision and Axapta Solutions in 2002, Microsoft entered the market for business solutions. At the time, Navision, now known as Dynamics 365 Business Central, aimed at Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs), and Axapta, now known as Dynamics 365 for Finance and Supply Chain Management focused on larger companies.
In today’s business application market, Microsoft offers Dynamics 365 Business Central and Dynamics Finance and Supply Chain along with many other Dynamics 365 apps which are designed as an attempt to thoroughly address all the complexities involved in implementing legacy ERPs. The responses have a significant impact on both the client and the technique of implementation, or the implementor. What then are these impacts referring to? Let’s discuss this in detail.
Despite the two systems’ differences, they have several characteristics that are typical of most conventional business solutions:
Infrastructure Deployment Vs On-Cloud Deployment
The ability of Dynamics 365 ERP solutions to be implemented on local infrastructure must be emphasized, as doing so obviously adds a significant deal of complexity. The implementer in this situation must create a thorough plan for the necessary hardware, system, and application software. Mechanisms for maintenance and updating must be established.
Easy and Fast Customisations
Earlier customisations were done mainly by directly changing the standard program code provided by Microsoft as generally, the standard functionality of an ERP sometimes doesn’t meet all the client requirements.
The Power Platform, on the other hand, is a “Low-Code Development Platform” that contains Power BI, PowerApps, Power Automate, and other services that make it possible to quickly create solutions for “self-service business intelligence,” application development, and automation.
Better Implementation Methodology
Implementation for the tools was backed by Waterfall Model where the phases involved can easily be charted as analysis, design, development, testing, training, and transition to production operations.
The Dynamics 365 suite of business apps is updated almost monthly, if not more frequently. Major changes are currently occurring, including the decomposition of large monolithic solutions, which manifests itself in the removal of entire modules in favor of new cloud solutions (recent examples include Dynamics 365 Human Resources, Finance Insights, and AI). In such a setting, it is impossible to imagine using rigid implementation methodologies to implement a complex business solution. Microsoft has developed a methodological approach dubbed CRP (Conference Room Pilot), which combines the waterfall and agile methodologies, in response to the environment’s rapid change.
Easy to upgrade and Scalable System
Change Management i.e., the hot-fixes, improvements., (updates to the standard solution) were provided throughout the support lifecycle of a tool version, was a complex task to implement On-premises infrastructure.
The complete liberty in code management and patch installation that we were common in legacy ERP solutions is not the case with cloud solutions. Application lifecycle management for Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations is only available through the LCS (Lifecycle services) collaboration site, which, in the case of cloud solutions, implies that Microsoft handles applying changes to the production environment as part of their regular services.
Periodic System Updates
Tool Upgradeswere primarily introduced over one or two years, which comprised both the technology and data structure which was a complex task to transit from older to the new version being an On-premises solution.
Updates include the ongoing addition of functionalities and features. Dynamics 365 users receives a certain number of updates periodically in a year. In addition, critical fixes are always available for the previous release.
Conclusion
Cloud ERP Systems allows the SMBs to access world-class software without the need for heavy investment cost on infrastructure, it’s backed with scalability and the businesses need not worry about updating the system as the vendor automatically releases periodic updates.
It helps the businesses in trimming operational expenses and increasing the ROI.
People Also Ask
What is the difference between Cloud ERP Vs Legacy ERP?
Servers owned or leased by the vendor host cloud ERP systems. Additionally, users use web browsers to access cloud ERPs. On the other hand, traditional ERP systems (on-premises) are housed on computers and servers that you, the user, own, rent, and operate. Your access is therefore restricted to those devices.
What is Cloud ERP Solution?
Software for enterprise resource planning, or cloud ERP, is accessed online. Cloud ERP software serves as the “brains” or “backbone” of an organization’s IT infrastructure, offering cutting-edge capability for all key business operations.
What benefits do cloud ERP systems have over traditional on-premises ERP systems?
To sum up, cloud-based ERP solutions offer seamless application integration, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness over older ERP solutions, making them far more sophisticated and cost-effective.
What are the reasons that businesses move from Legacy ERP to Cloud ERP?
- Old Features
- Obsolete Technologies
- Higher Cost of Operations
- Functional Disparities
- Maintenance Cost
- Limited Information Access
What are the advantages of Cloud ERP?
- Easy to scale
- Round the clock support
- Low Maintenance Cost
- Higher Security
- Real-Time Data Reporting
- Accessible from any device, anywhere

Witness a scalable transformation
Experience real-time synchronisation and flexibility with a consistent view across your business.
Disclaimer– “All data and information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only. Dynamics Square / MPG Business Information Systems Pvt. Ltd. makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, currentness, suitability, or validity of any information on this site and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use.”

.jpg)